Data mapping maturity is your organization’s level of data mapping automation. The higher the level of automation, the higher the maturity level. There are two levels of data mapping maturity, and we will discuss these individually to help you understand them better.
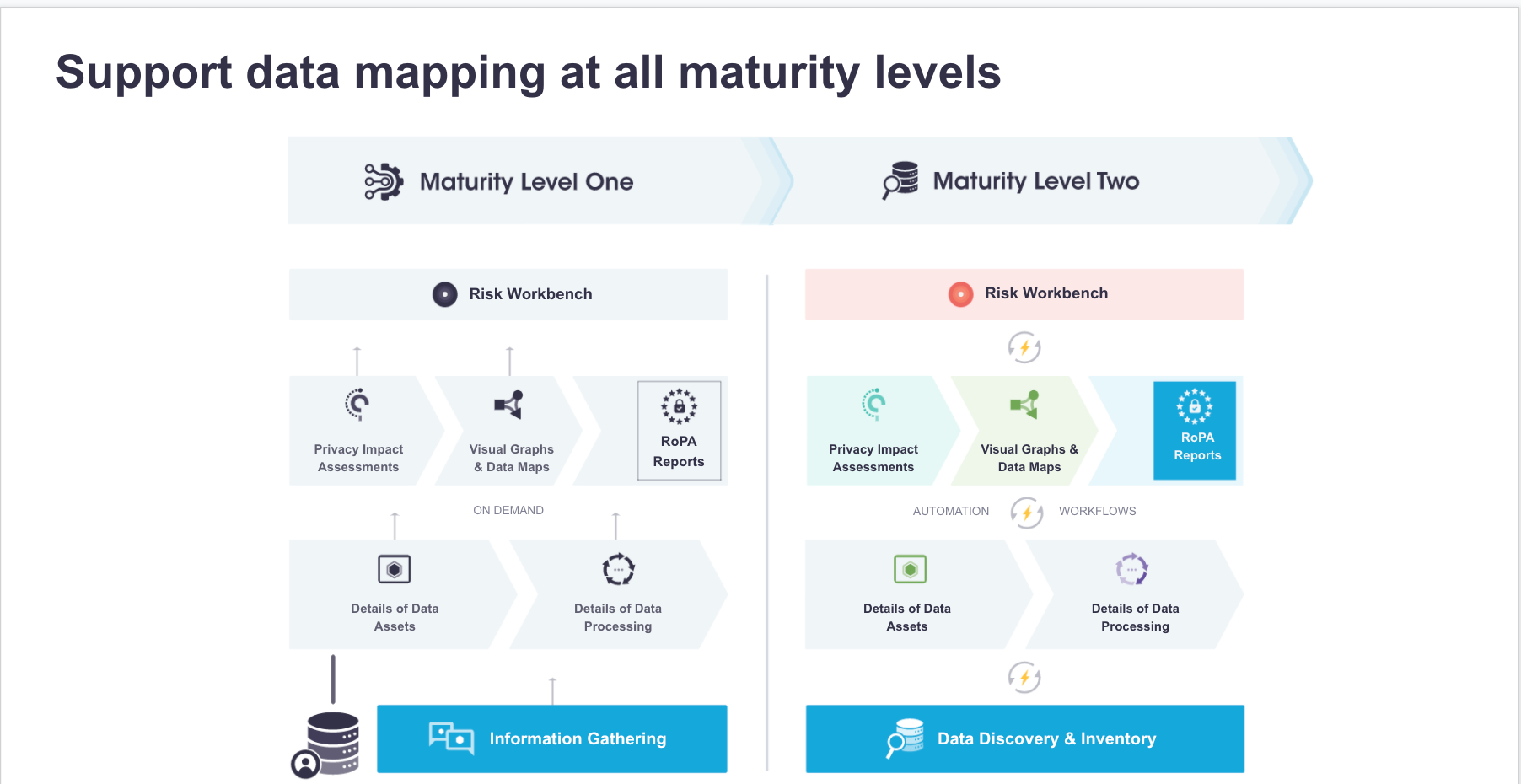
Many organizations currently use manual and legacy techniques to build and develop a data map. As previously explained, these systems are not only time-consuming, but they also increase the risk of PI data sprawl into other systems. This is where the PrivacyOps Data Mapping platform can step in.
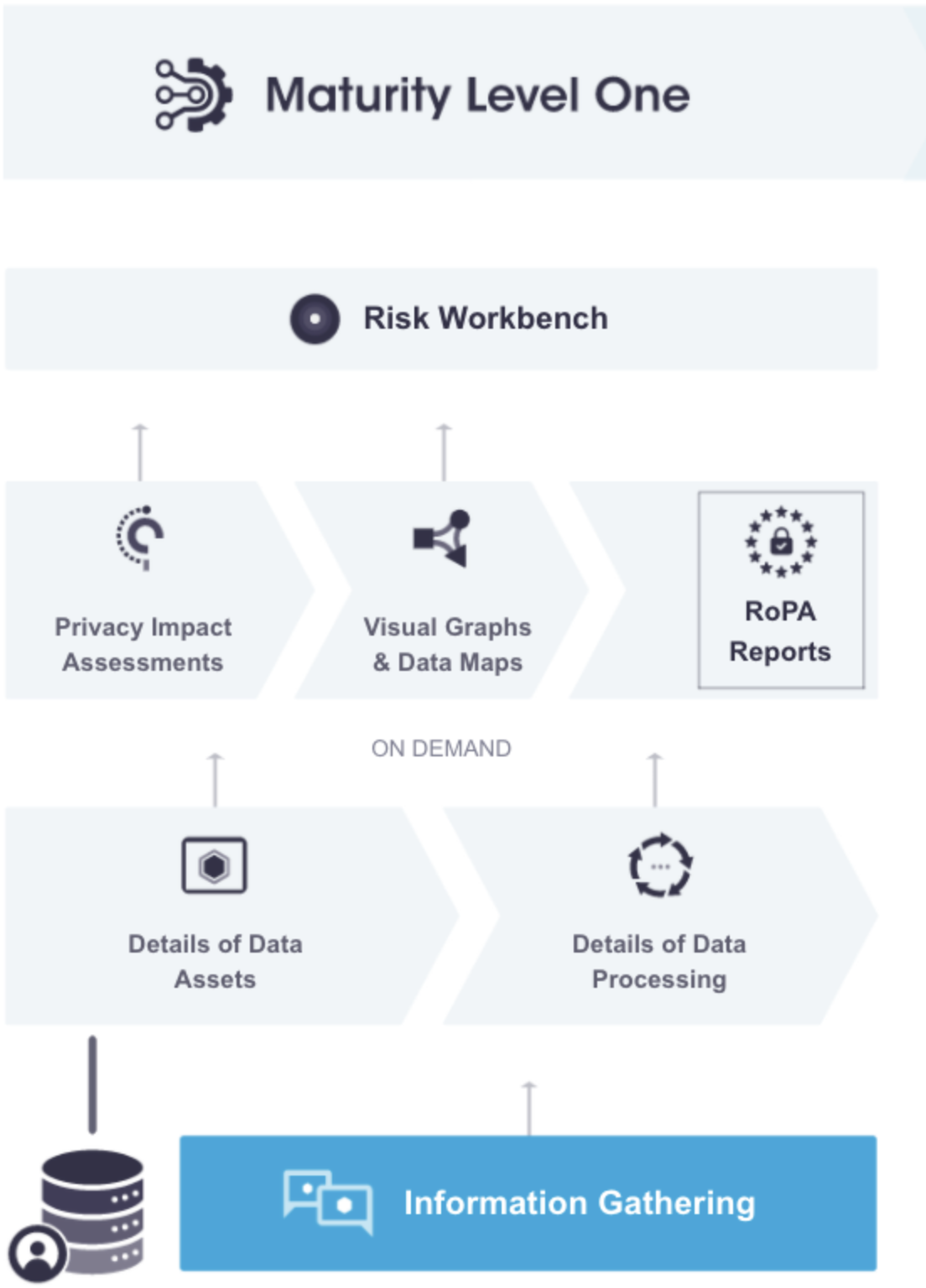
While full automation is the ultimate goal of PrivacyOps compliance, organizations need time to adjust and migrate their existing processes to this new paradigm. Maturity Level 1 helps organizations transition and ease into using the PrivacyOps data mapping platform. Organizations can update their system of record to a more modern, consolidated, collaborative, and intelligent system while retaining their existing processes for manual input and construction of the data map.
It is important to note that Maturity Level 1 only provides minimum automation (workflow automation, dynamic visual data maps, automated Article 30/RoPA reports) and is the first step in the PrivacyOps framework.
Organizations can populate their data maps catalog with new and existing assets, vendors, and institutions through:
| Data Assets | Vendors |
| SaaS applications and data stores are used to collect, store, and process personal information. You must manually create entries and capture as many details/attributes of these assets. | These represent relationships with suppliers and vendors who offer assets and services or act as sub-processors for your organization. |
| Institutions | Processes |
| These are controllers, processors, joint controllers, and data recipients when you sell data. You might also use them to identify entities that act as sources, storage locations, and data destinations. | Every process has three fundamental aspects from your data catalog: A source, an asset, and a destination for the data. These are combinations of the elements described above that show your data process flow in graphic and tabular forms. You create processes between assets, vendors, and institutions using connectors. |
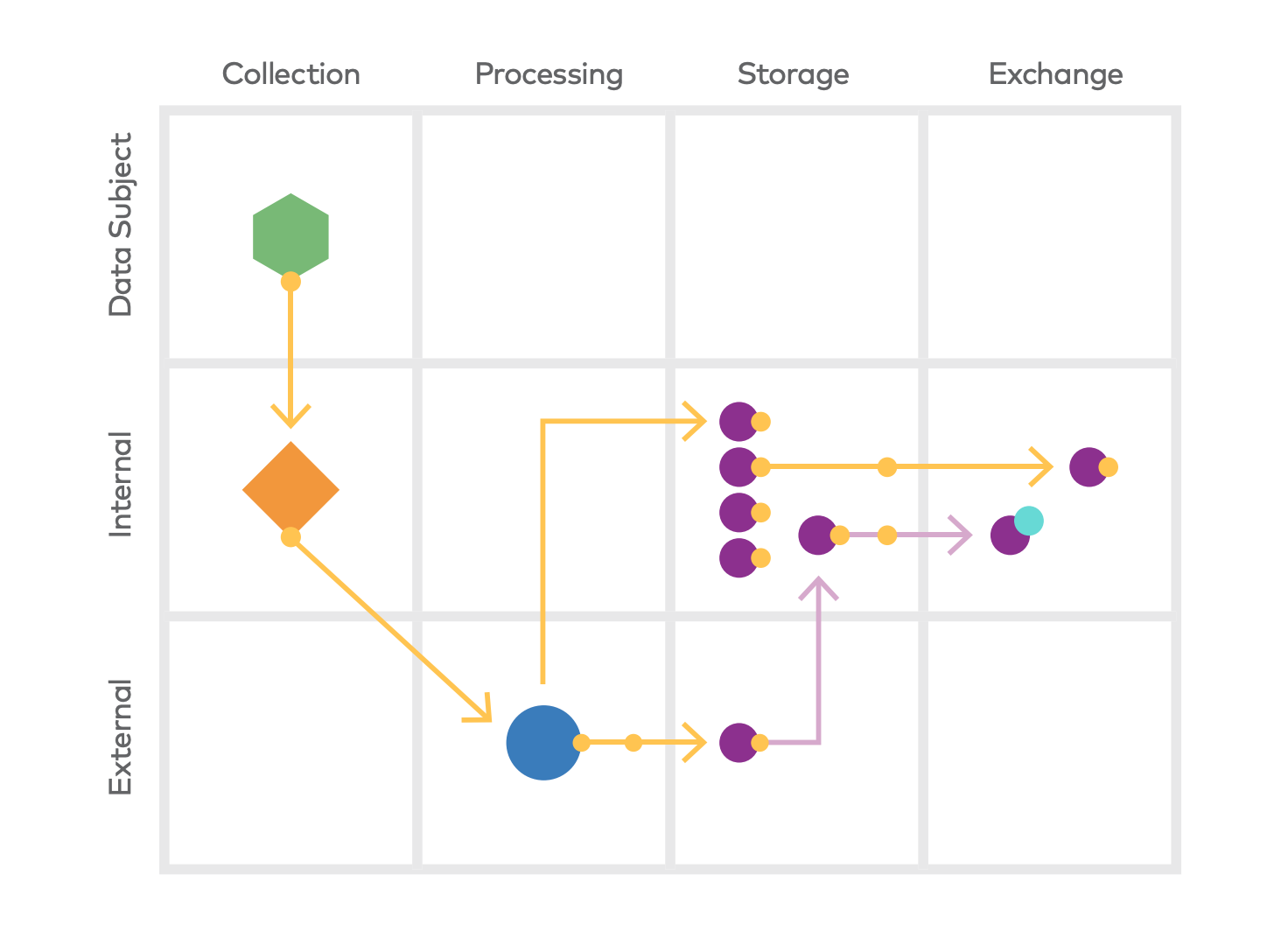
The relationships between the various assets, vendors, and institutions within the data mapping catalog are generally classified as either processes or data flows. Organizations must record these relationships within a data map for a holistic picture of the personal data. These processes or data flows can be recorded through:
Once a data catalog:
Then organizations can create automated Record of Processing Activities (ROPA) reports – which are mandatory under most major privacy laws – such as under Article 30 of the GDPR.
These reports essentially document the processing activities and the flow of personal data that is collected, retained, or received by the organization.
The PrivacyOps Data Mapping Maturity Level 1 allows organizations to consolidate their manual data mapping efforts onto a single and secure technology platform. The platform is more efficient than legacy systems such as spreadsheets. Many processes recorded using legacy data mapping systems may be quickly outdated because of the dynamic nature of modern data processing activities.
Similarly, data mapping at Maturity Level 1 might still leave significant gaps as there is an increasing risk of missing essential data assets or attributes using manual techniques.
Organizations can use automated data mapping to ensure consistency of the information documented on a data map by shifting to Maturity Level 2. At this level, organizations leverage AI-powered automation and data intelligence to construct and maintain comprehensive, holistic, and dynamic data maps by:
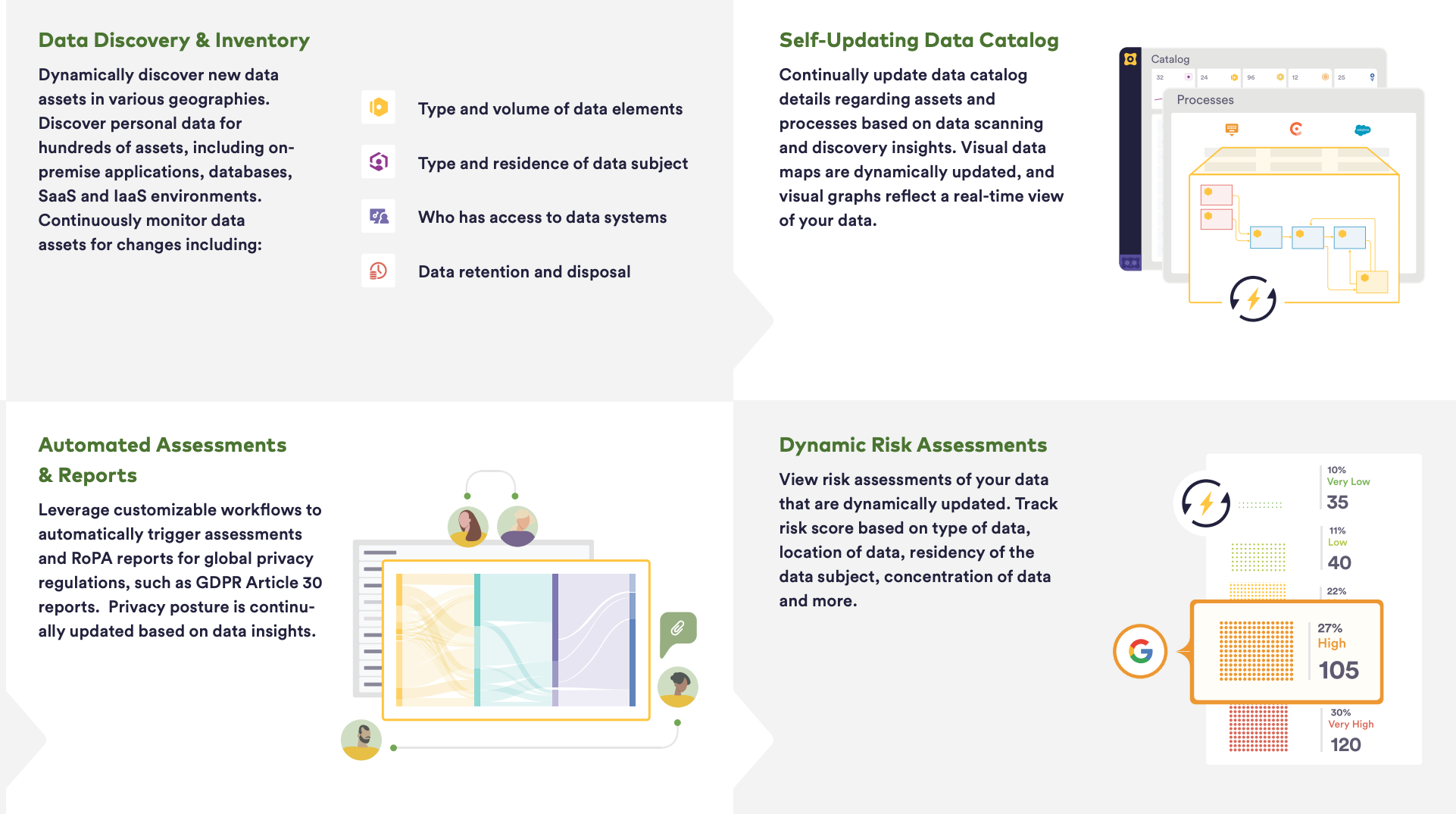
Data Mapping Maturity Level 2 helps create dynamic, holistic, and updated data maps that can be used as a foundation for PrivacyOps compliance and ensure Privacy by Design principles are implemented across your organization. When an organization’s data is fully mapped, fulfilling DSR requests and other regulatory requirements becomes easy and efficient.
Robotic automation helps organizations improve their PrivacyOps compliance with automated Risk Assessments, Privacy Policy Creation and Management, Universal Consent, Data Subject Rights Fulfillment and Data Breach Management, and Cookie Consent. These privacy products help organizations address data privacy regulations worldwide. Undertaking a data mapping activity using the PrivacyOps platform provides the much-needed foundation for all other PrivacyOps operations using advanced AI-powered automation and data intelligence.
Another example of a more advanced feature that results from Data Mapping Automation is People Data Graphs (PDGs). These Data Graphs help:
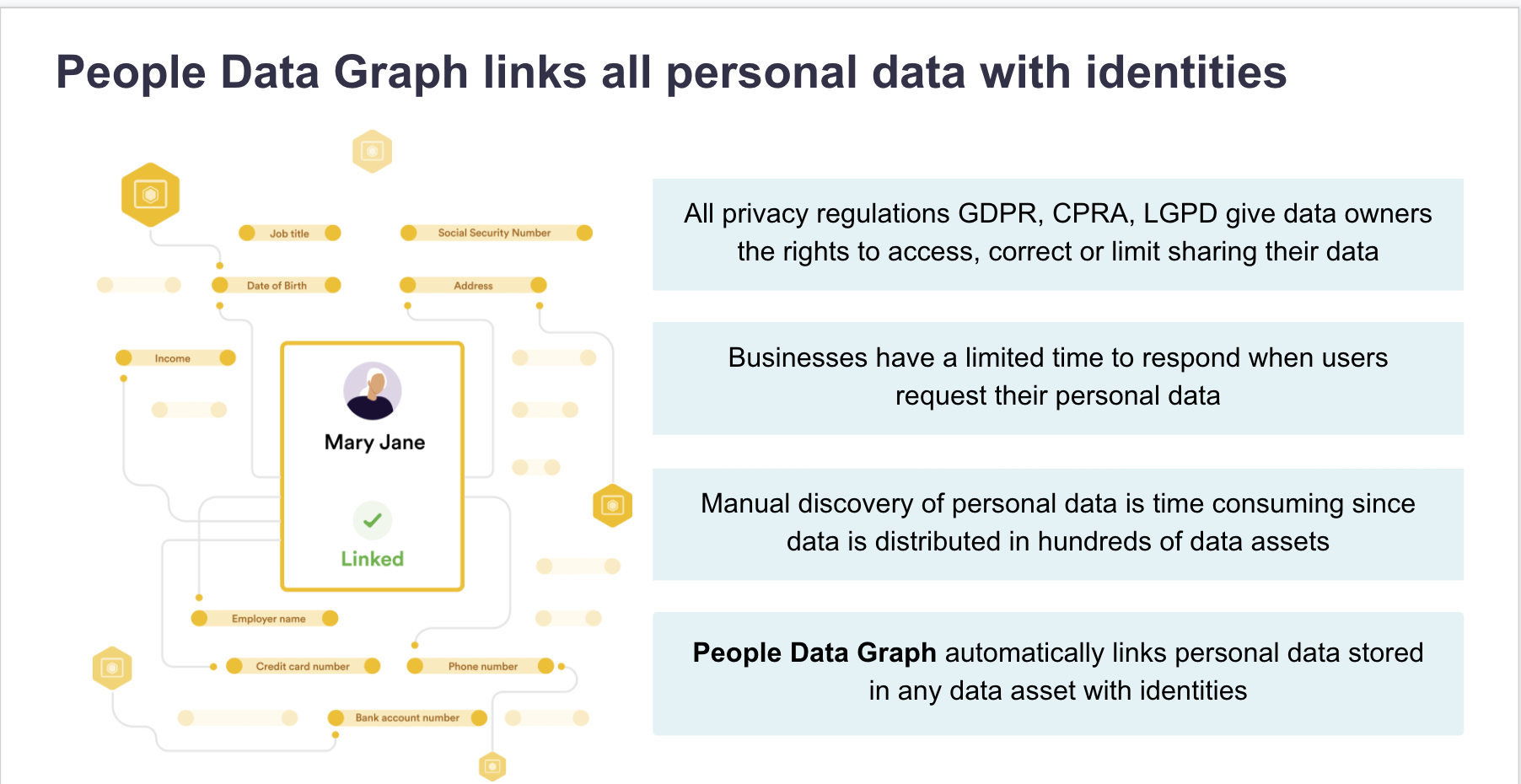
Automated DSAR fulfillment saves organizations time, money and strengthens brand trust resulting in improved customer loyalty. You will read more on this in the next module.
[email protected]
Securiti, Inc.
3155 Olsen Drive
Suite 325
San Jose, CA 95117