Now that we have understood why organizations need Sensitive Data Intelligence and what benefits it serves, let’s look at the adoption process stepwise.
The first step in Sensitive Data Intelligence is to gather and build a catalog of all cloud-native and non-native data assets. This data could be across SaaS applications, structured and unstructured IaaS data stores across multiple cloud providers, or on-premises.

The following steps help organizations build their comprehensive data asset catalog:
| Benefits of data asset discovery and building the data catalog | |
| 1 | Out-of-the-box discovery of hundreds of sensitive data attributes. |
| 2 | A central repository of data assets. Without a central repository of data assets, organizations have no way to know where personal and sensitive data is stored and how it is protected. |
| 3 | The CMDBs are automatically and periodically scanned to ensure that data assets are kept up-to-date. |
| 4 | An enriched asset catalog helps organizations comply with cybersecurity frameworks such as CIS, NIST, and many others that require organizations to maintain an up-to-date inventory of their data assets. |
Every data asset has various metadata that can be classified into business, technical, and security categories. Sensitive Data Intelligence provides native connectors and REST-based APIs to scan and extract metadata, including all business, technical and security metadata associated with each asset. With this metadata, organizations can determine how their Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Personal Health Information (PHI), and similar sensitive data are protected and governed.
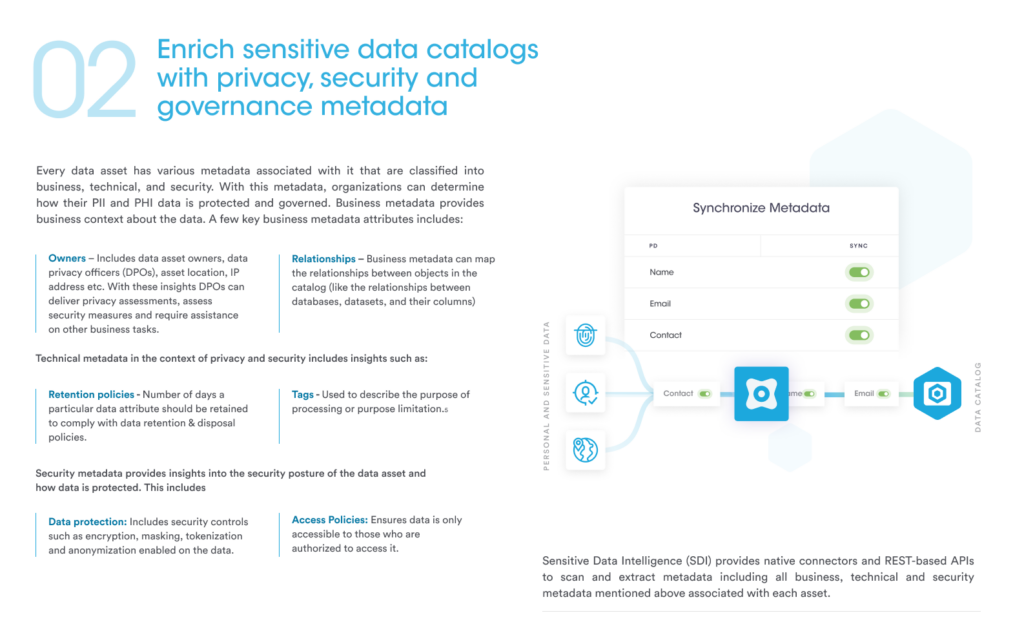
| Benefits of enriching sensitive data categories with privacy, security and governance metadata | |
| 1 | It provides more context and understanding to datasets. |
| 2 | It provides more insights into how a particular dataset should be handled, shared, and protected depending on its metadata category. |
| 3 | Retention labels within metadata manage the retention and disposition of data and control for how long the organization should keep a particular dataset and how the organization should handle it after the expiry of the retention period. |
Once all assets and their metadata have been cataloged, the next step is to enrich these assets with insights about sensitive data stored in them. Sensitive data is a specific set of personal data that requires additional protection compared to other data types. Since sensitive data needs to be protected and managed separately from different kinds of personal data, it is paramount for organizations to detect and identify all sensitive data stored in their data assets.
Let’s look into some of the types of personal and sensitive data.
| Types of personal and sensitive data | |
| Personal data | Any information relating to an identified or identifiable person. For example, name, email, phone number, social security number, driver’s license number, passport number, postal address, location data, or IP address. |
| Healthcare | Health-related data that the organization can use to identify an individual such as medical record number, insurance number, medical images |
| Financial | Any financial information associated with users such as credit card numbers, account numbers, PINs, etc. |
| Educational | Educational and academic records such as degrees, courses, disciplinary records, dates of attendance. |
Since personal and sensitive data is distributed across hundreds of data assets, the process of finding specific data attributes can be highly complex and time-consuming. Sensitive Data Intelligence helps organizations find specific data attributes within minutes across all structured and unstructured data stores. It also allows organizations to detect unique attributes that have specific requirements under global privacy laws.
This particular step involves detecting sensitive data in structured and unstructured data stores using in-built data attributes or custom attributes via a comprehensive detection engine. It has the following components:


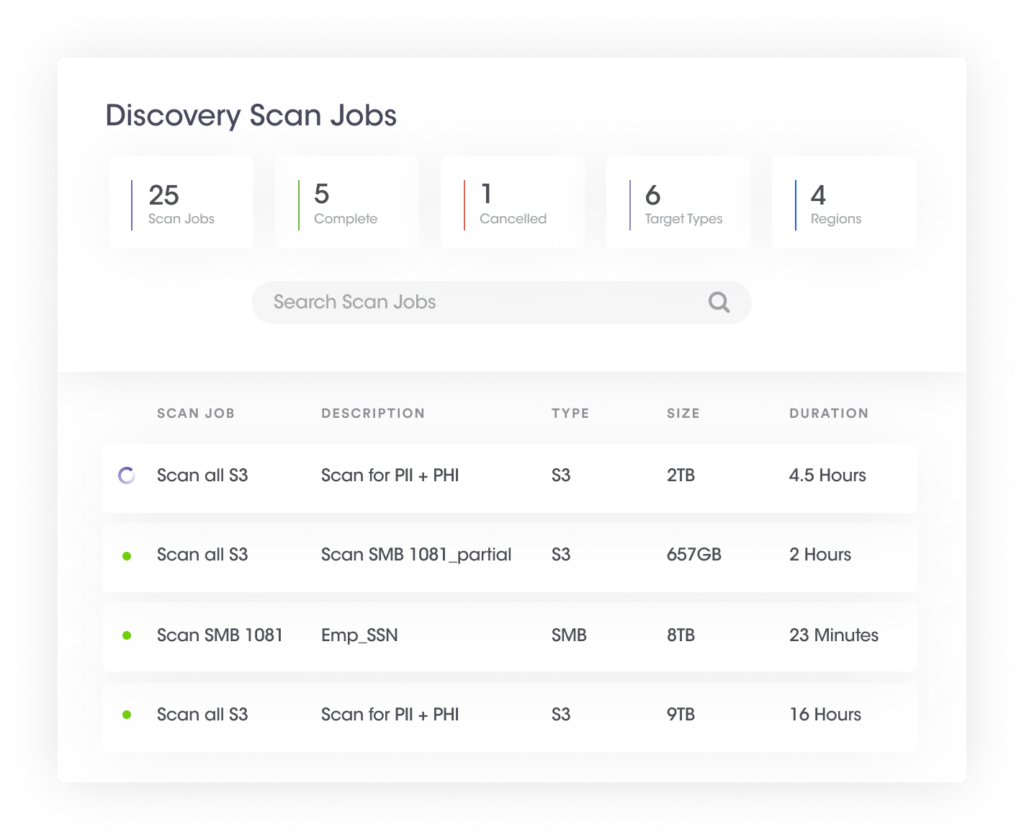
| Benefits of discovering sensitive and personal data across structured and unstructured assets | |
| 1 | Highly accurate and fine-grain document classifications in unstructured systems |
| 2 | Highly accurate column classifications in structured systems. |
| 3 | The organization can run multiple data discovery scans in parallel based on business requirements. |
| 4 | Granular customization, data sampling, and targeting for high-speed scans. |
Once sensitive data has been discovered from structured and unstructured data stores, the next step in Sensitive Data Intelligence is to enhance the sensitive data with automated classification and tagging. Sensitive Data Intelligence leverages machine learning technologies and natural language processing to deliver highly accurate auto-classification of datasets and data labeling. An extensible policy framework is used to automatically apply sensitive labels and metadata to files/documents for various use-cases.
The following steps help you achieve this:
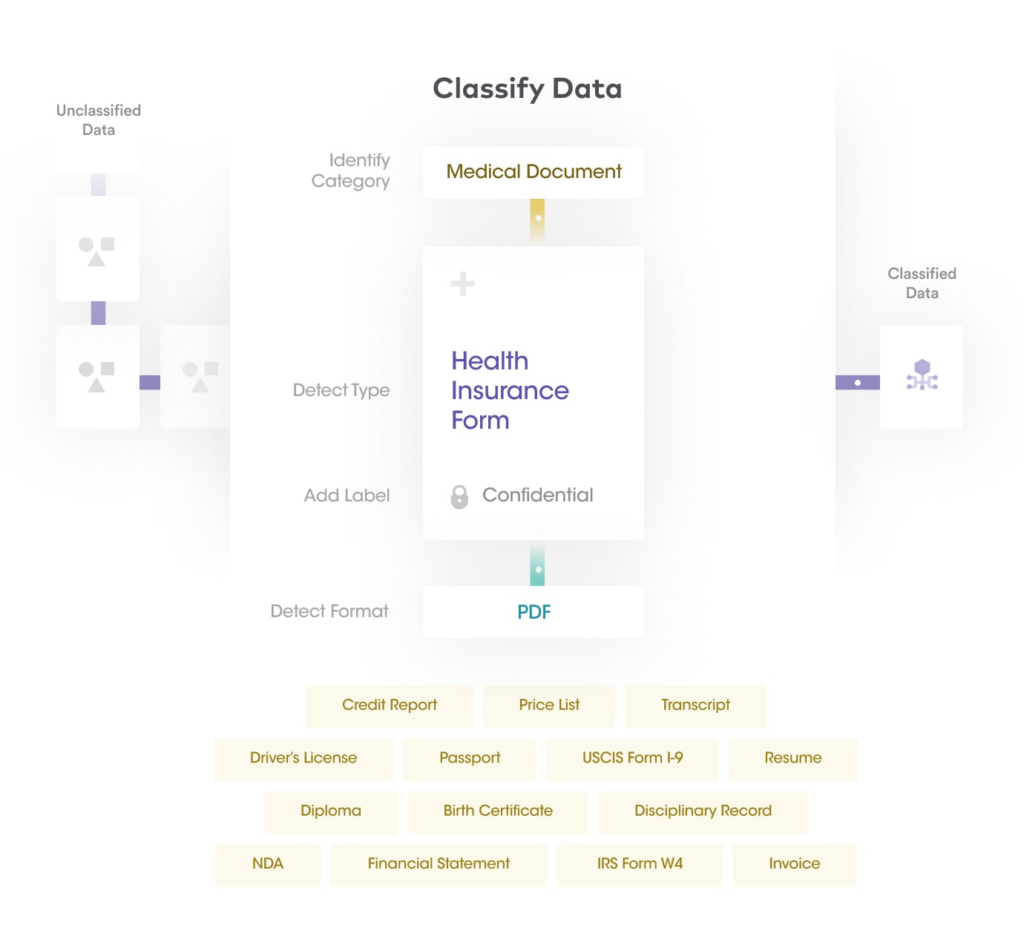
| Benefits of developing sensitive data catalog with automated classification and tagging | |
| 1 | Based on the functional categorization of data, an organization can determine which privacy and security regulations apply to those datasets. |
| 2 | A data classification policy can be maintained that will help organizations demonstrate how particular data should be managed, shared, and protected. |
| 3 | Tags and labels enable organizations to find and report on data held for various purposes required by privacy regulations. |
Once your asset catalogs have been enriched, the next step is to manage your security posture across your multi-cloud data assets, various SaaS applications, and on-premise clouds to ensure your data environment is secure.
Sensitive asset and data posture management help organizations gain visibility and configuration monitoring of data assets while ensuring adequate security settings. Organizations can scope configuration settings based on the sensitivity of data in them. For example, disabling public access data settings is required for data containing confidential information. However, data containing an organization’s website materials should have public access. Also, applying selective security settings based on the data’s sensitivity helps lower cost and management overhead. For example, enabling Cloudtrail or Server access logs broadly on all data is unnecessary and expensive, and the organization may only need it for regulated data for compliance audits.
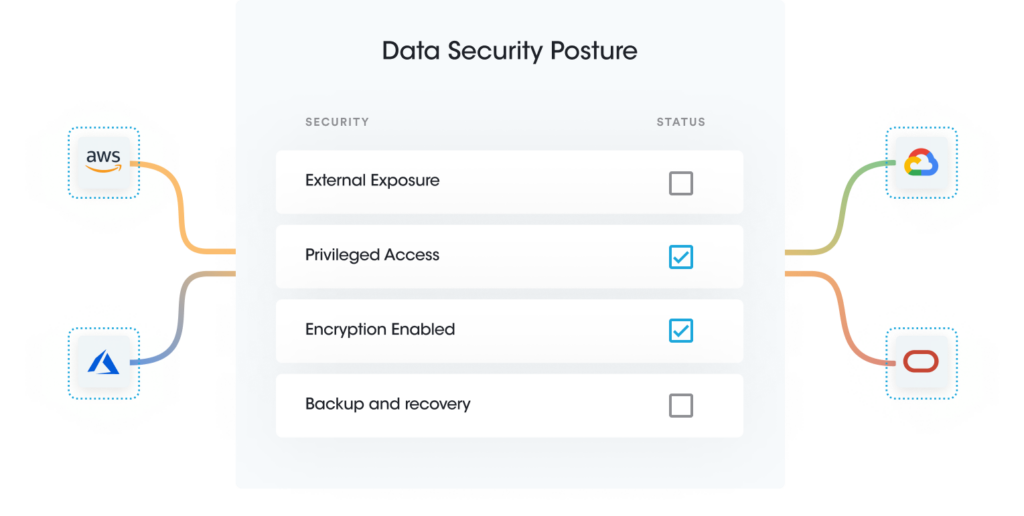
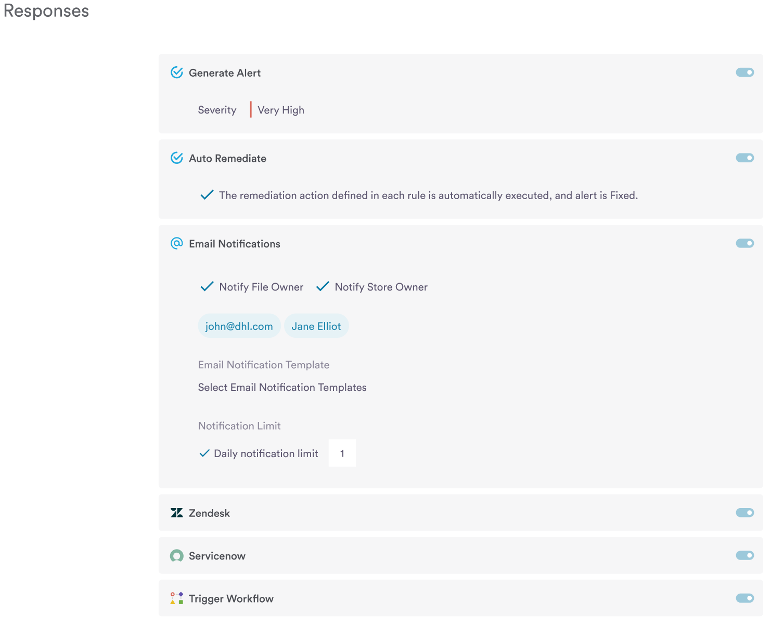
Dynamic enterprise environments require continuous data discovery scans to ensure regular security posture monitoring and compliance. Sensitive Data Intelligence provides the ability to monitor Sensitive Assets and Data Posture continuously. It also enables auto-remediation to resolve security risks instantly.
As a result of these processes, an organization can automate security and privacy controls. Once an organization has gained visibility into its data security posture, it can discover gaps in its security controls and orchestrate appropriate security controls to fill the gaps.
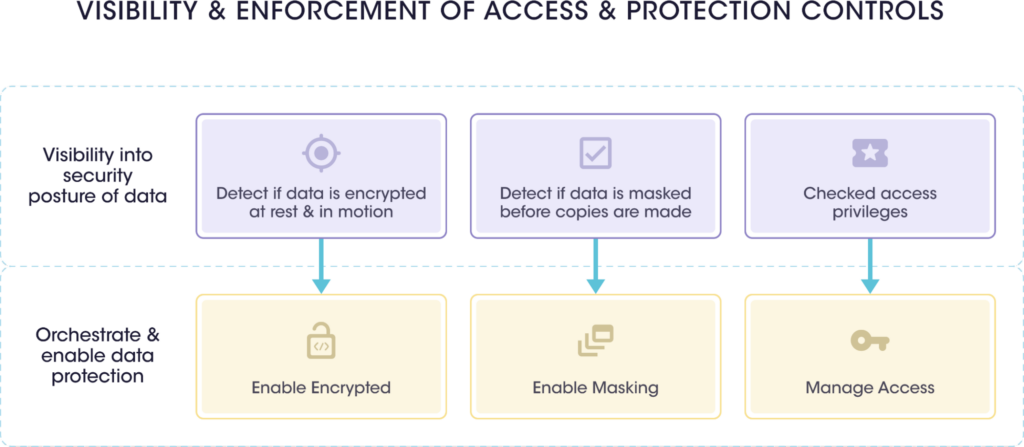
| Benefits of Sensitive Asset and Data Posture | |
| 1 | It provides visibility into the security posture of data and enables data protection. |
| 2 | Organizations can choose appropriate mitigation measures and security controls depending on the nature of data to be protected and its sensitivity. |
It becomes challenging for organizations to determine which data poses the most significant security and privacy risks with a data glut. However, for continuous data security and compliance purposes, organizations need to understand the inherent risk of the data. Without a clear understanding of data risks, an organization may misallocate budgets and resources for risk mitigation activities and security controls.
This step provides an executive summary of an organization’s data risks in the form of a data risk graph. It provides a single numerical figure depicting the overall data risk.
This step has the following processes:
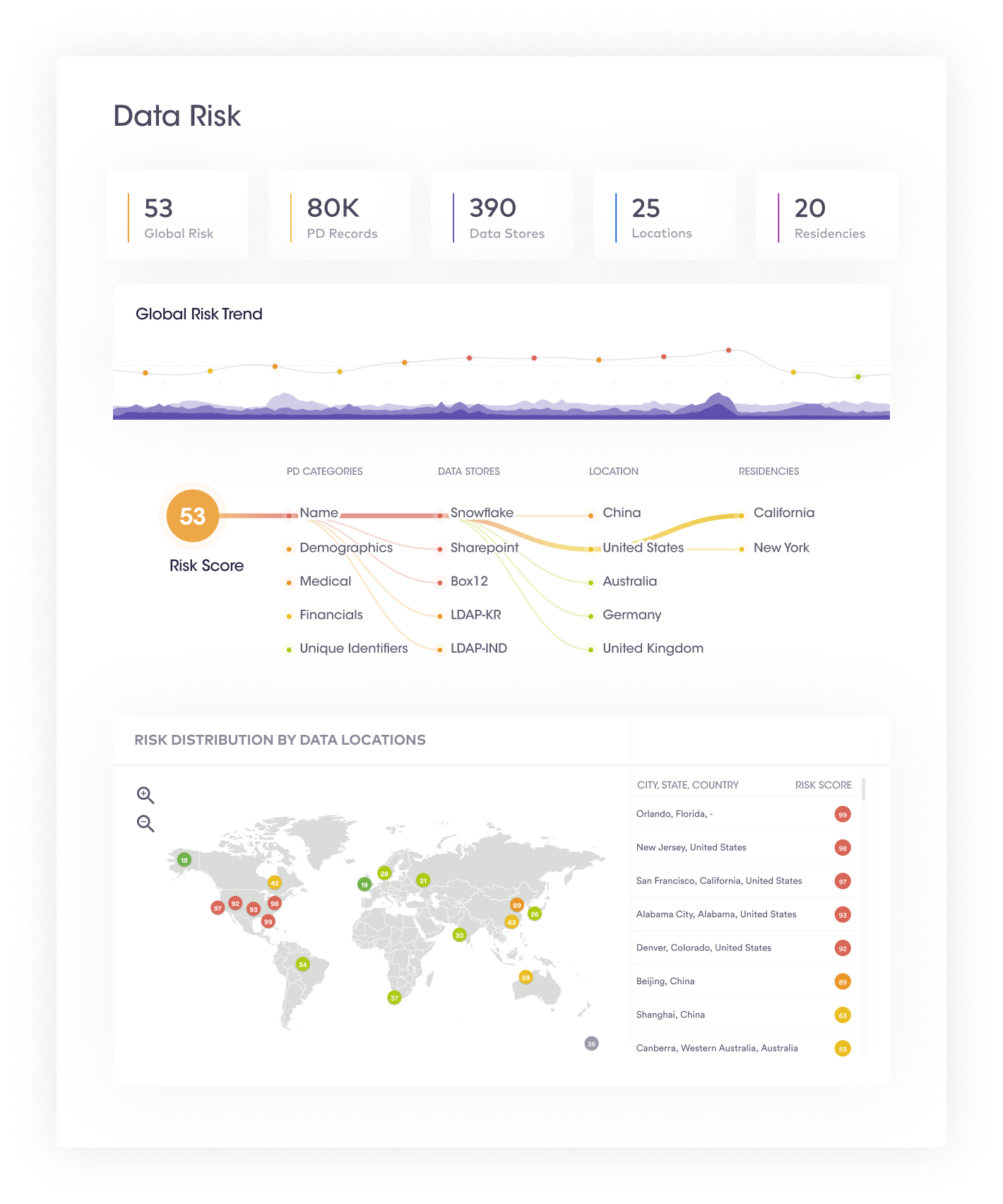
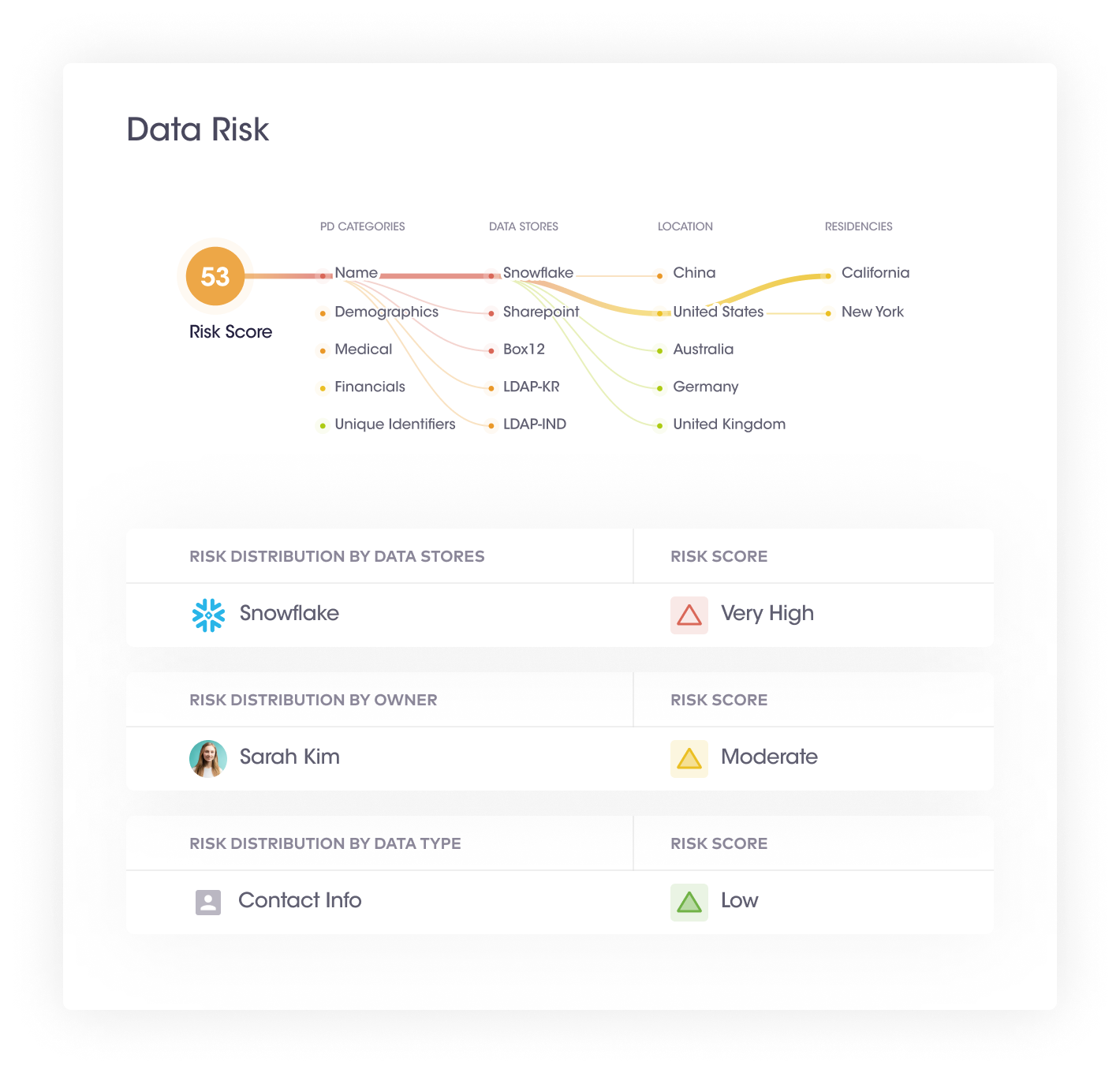
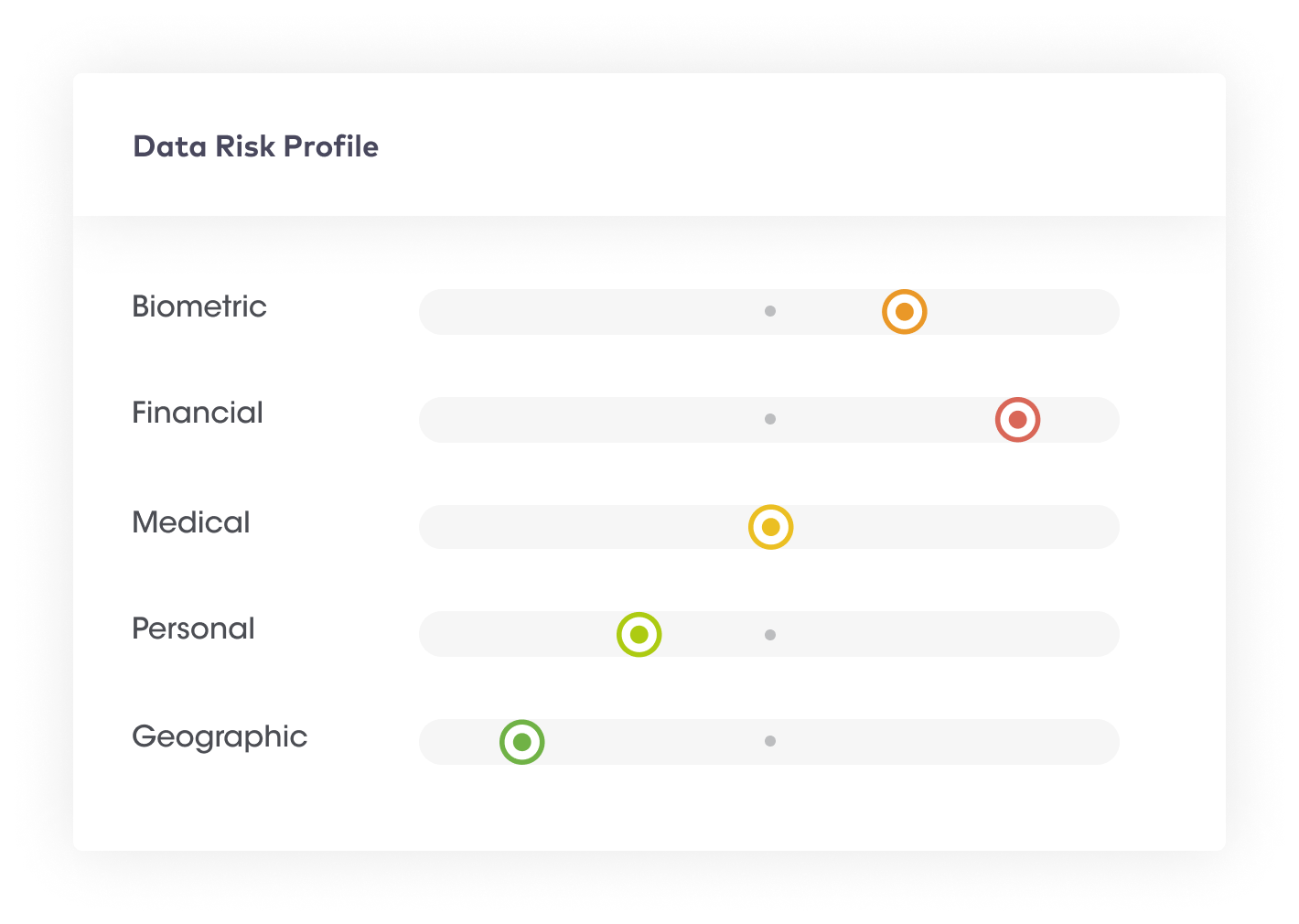
| Benefits of data visualization, identification of high-risk assets & configuration of data risks | |
| 1 | Organizations can take immediate containment and mitigation actions even before a security incident has taken place. For example, if a large amount of sensitive data appears in the data system, a spike in the risk score can alert organizations to take proactive actions. |
| 2 | Tracking global data risk scores can help organizations uncover high-risk activities and whether or not risk scores have reduced over time. |
This step is the final stage of Sensitive Data Intelligence and is paramount in ensuring compliance with global privacy laws. It involves building a People-Data-Graph to map personal data with its correct owners, i.e., customers, users, employees, and other individuals. People-Data-Graph is a graph between an individual and their personal data across all connected systems. It is an easy-to-use conversational interface.
This step has the following processes:
| Benefits of building a relationship map between data and their owners | |
| 1 | This step enables organizations to fulfill DSR requests within days instead of weeks or months and increase customer’s confidence about their privacy practices. |
| 2 | This step enables organizations to create relevant DSR and data breach reports in a secure portal, reducing personal data sprawl. |
[email protected]
Securiti, Inc.
3155 Olsen Drive
Suite 325
San Jose, CA 95117